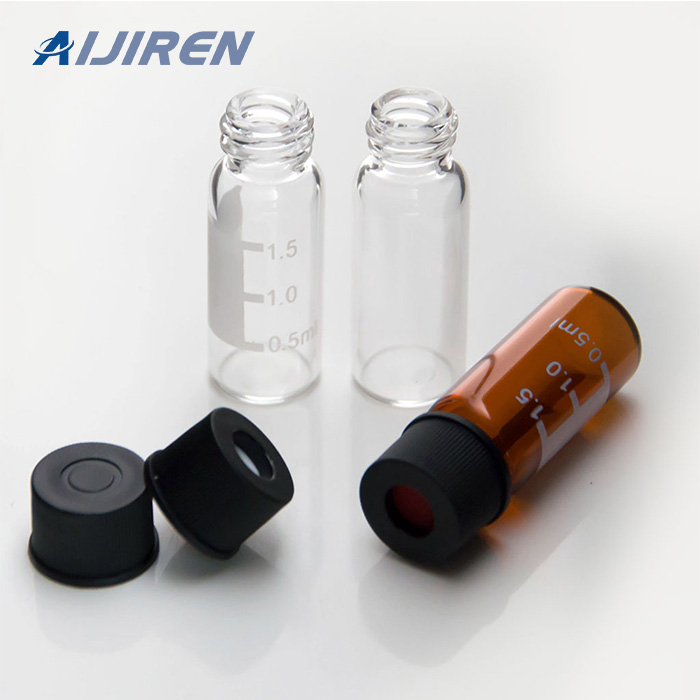
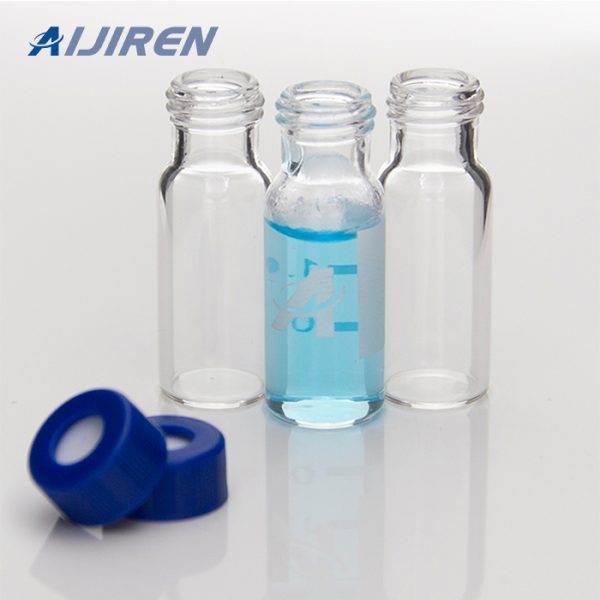
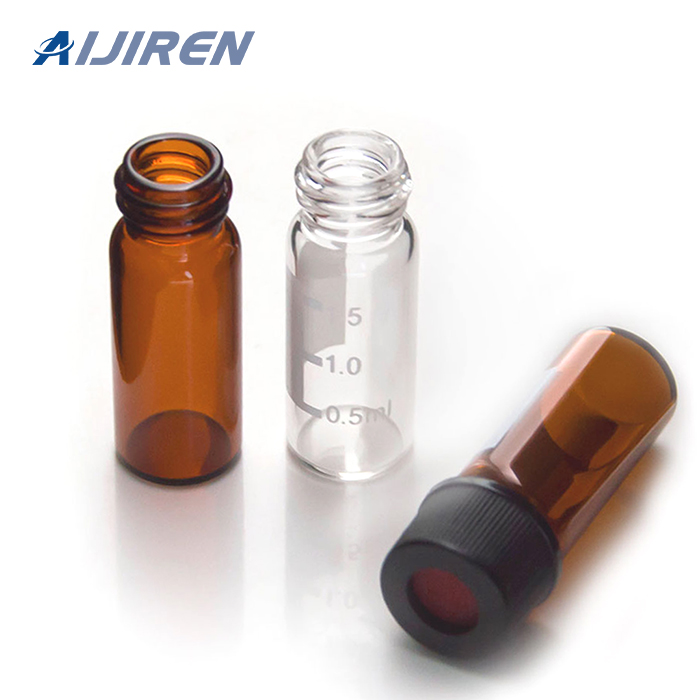
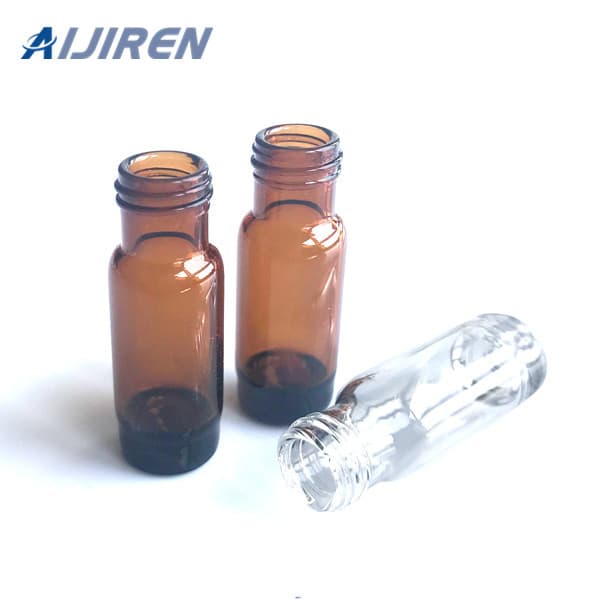
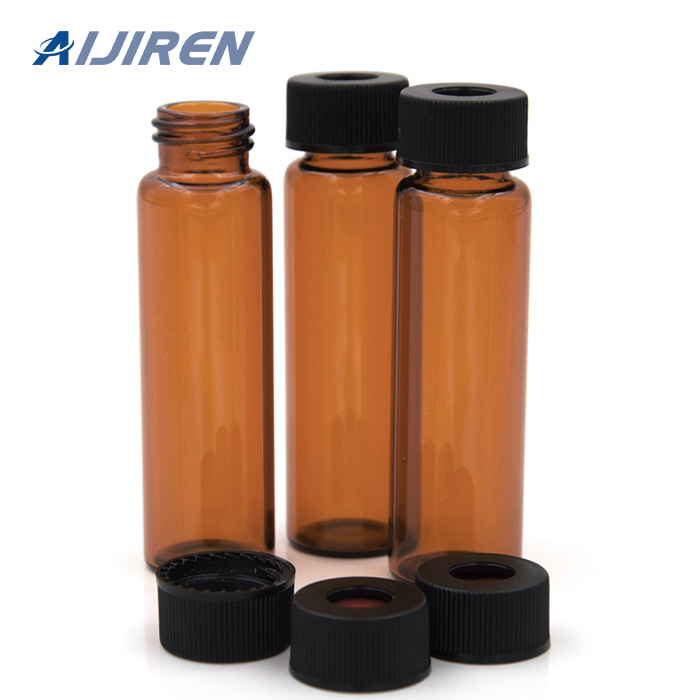
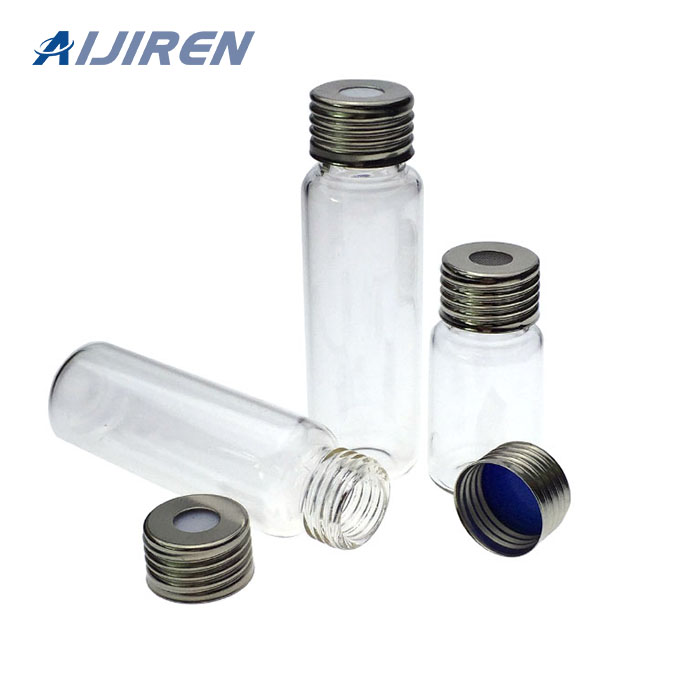
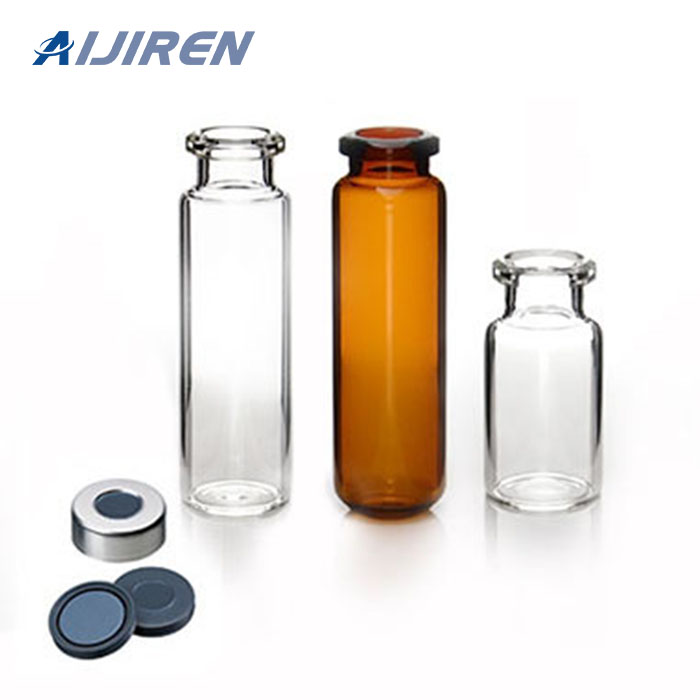
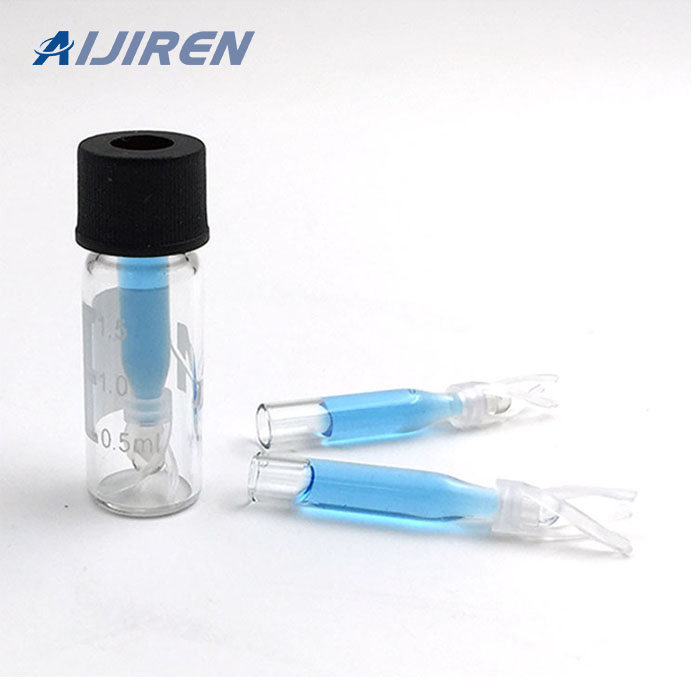
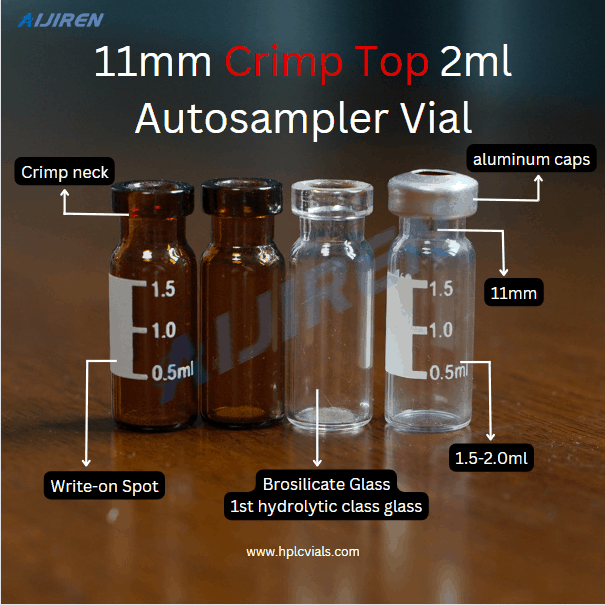
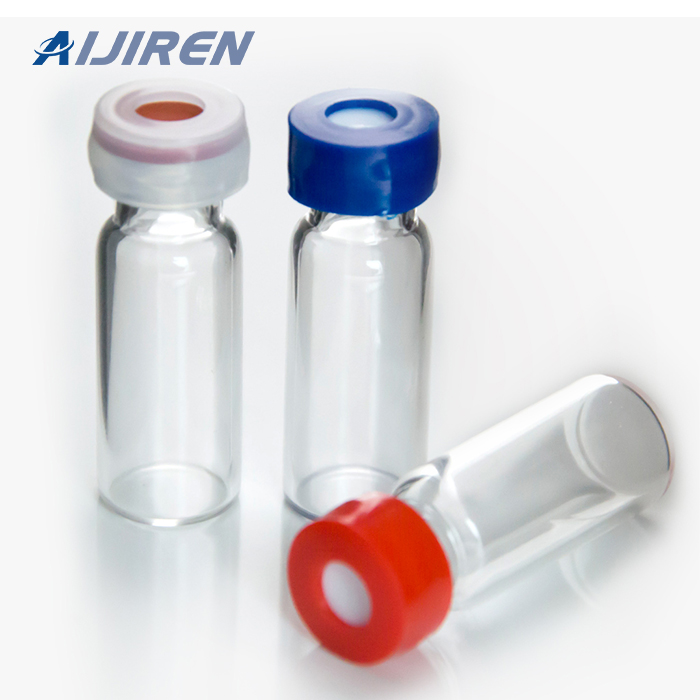
Vials are small containers typically used to store and transport liquids. There are various types of vials designed for different purposes.
what is the difference between tube and vials?
Tubes and vials are both types of containers used for various purposes, and while there may be some overlap in their uses, there are distinct differences between the two:
Tubes:
- Shape: Tubes are generally elongated cylindrical containers with open ends. They can be open at both ends or have one end sealed.
- Closure: Tubes often have a removable cap or stopper that can be easily taken off and put back on.
- Applications: Tubes are commonly used for storage, transportation, and handling of liquids, powders, or small items. They can be made of materials such as plastic, glass, or metal.
Vials:
- Shape: Vials are typically smaller, more compact containers with a narrow neck and a small opening. They can be cylindrical or have other shapes.
- Closure: Vials usually have a tight-sealing mechanism, such as a screw cap or snap cap, to ensure the contents remain secure and uncontaminated.
- Applications: Vials are commonly used in laboratories, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare for storing and transporting small amounts of liquids, samples, or medications. They are often made of glass or plastic.
In summary, the main differences lie in the shape, closure mechanism, and specific applications. Tubes are more versatile and can have open ends, while vials are designed for secure containment, especially in fields where maintaining the integrity of the contents is crucial, such as in laboratories or healthcare setting.
How are vials labeled?
Vials are labeled to provide important information about their contents, usage, and other relevant details. The labeling process for vials can vary depending on the industry, regulations, and specific requirements. Here are common methods and information included in vial labeling:
- Label Material: Labels for vials can be made of paper, plastic, or other materials, depending on factors such as the intended use, storage conditions, and regulations.
- Printed Information: The label typically contains printed information, including:
- Product Name: Clearly stating what is contained in the vial.
- Dosage/Concentration: Indicating the strength or concentration of the substance.
- Lot Number: A unique identifier for tracking and quality control.
- Expiration Date: The date until which the contents are expected to remain stable and effective.
- Manufacturer Information: Identifying the company or entity that produced the vial.
- Usage Instructions: Instructions for proper use, administration, or handling.
- Barcodes and QR Codes: Many vials have barcodes or QR codes that facilitate automated tracking, inventory management, and authentication.
- Regulatory Information: Compliance with regulatory standards often requires specific information to be included on the label, such as warnings, precautions, and regulatory symbols.
- Tamper-Evident Features: For pharmaceuticals and other critical applications, vial labels may include tamper-evident features to indicate if the vial has been opened or tampered with.
- Batch or Production Date: Providing information about when the vial was manufactured.
- Storage Conditions: Instructions on how the vial should be stored (e.g., temperature requirements) to maintain product stability.
- Language and Symbolic Representation: Labels may include information in multiple languages, and symbolic representations for ease of understanding, especially in international markets.
- Color Coding: In some cases, color-coding may be used to quickly identify different types of vials or their contents.
It’s essential for vial labeling to comply with relevant regulations, such as those set by health authorities or industry standards, to ensure safety, traceability, and proper use of the contents.